Oligohydramnios Nanda Nursing Diagnosis
Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care is referred to as oligohydramnios. Oligohydramnios is diagnosed based on ultrasound measurements of amniotic fluid Amniotic fluid A clear, yellowish liquid that envelopes the fetus inside the sac of amnion. In the first trimester, it is likely a transudate of maternal or fetal plasma.
Oligohydramnios causes, diagnosis and treatment in pregnancy
Assessment Types of Trauma Open Wounds Blunt Abdominal Trauma Gunshot Wounds Poisoning Choking Orthopedic Injuries Burns Respiratory Disorders in a Pregnant Woman Acute Nasopharyngitis Influenza Pneumonia

OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS II PROBLEM DURING PREGNANCY II NURSING ACADEMY YouTube
The diagnosis of oligohydramnios is made via ultrasound examination. There are two ways of measuring amniotic fluid; amniotic fluid index (AFI) or maximum pool depth (MPD). They have similar diagnostic accuracy, however AFI is more commonly used.

PPT Oligohydramnios PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9464009
Oligohydramnios means that, relative to gestational age (meaning how far along the pregnancy is), the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus (baby) is at low levels. Amniotic fluid is the water that surrounds the fetus in the uterus. At the start, it contains mostly water with electrolytes.

Oligohydramnios Nanda Nursing Diagnosis
Diagnosis. A diagnosis of Oligohydramnios is established based on medical history, clinical evaluation, and investigation results. A diagnosis of Oligohydramnios has been suspected if the amniotic fluid is less than 8 cm on ultrasound and is confirmed if it is less than 5 cm. Other diagnostic indicators are as follows:

Oligohydramnios
Clinical features History Oligohydramnios is diagnosed via ultrasound during routine pregnancy monitoring. The history can vary depending on the cause and each woman may experience symptoms differently or may experience no symptoms at all.

Oligohydramnios Nursing school survival, Nursing school motivation
Potter's syndrome. The fetal kidneys fail to develop or have malformation such as the absence of one or both kidneys (renal agenesis). Placental insufficiency. The blood from the placenta is redistributed to the fetal brain rather than the abdomen and kidneys, causing decreased fetal urine output. Fetal gastrointestinal anomalies.

NCP 32 Nursing care plan on Oligohydramnios/ Gynecological Disorders
Oligohydramnios. Oligohydramnios is amniotic fluid volume that is less than expected for gestational age; it is associated with maternal and fetal complications. Diagnosis is by ultrasonographic measurement of amniotic fluid volume. Management involves close fetal monitoring and serial ultrasonographic assessments.

OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS Causes and Treatment
Oligohydramnios is a condition of abnormally low amniotic fluid volume that has been associated with poor pregnancy outcomes. To date, the prevalence of this condition and its outcomes has not been well described in low and low-middle income countries (LMIC) where ultrasound use to diagnose this condition in pregnancy is limited. As part of a prospective trial of ultrasound at antenatal care.
Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios USMLE Step 2 Review YouTube
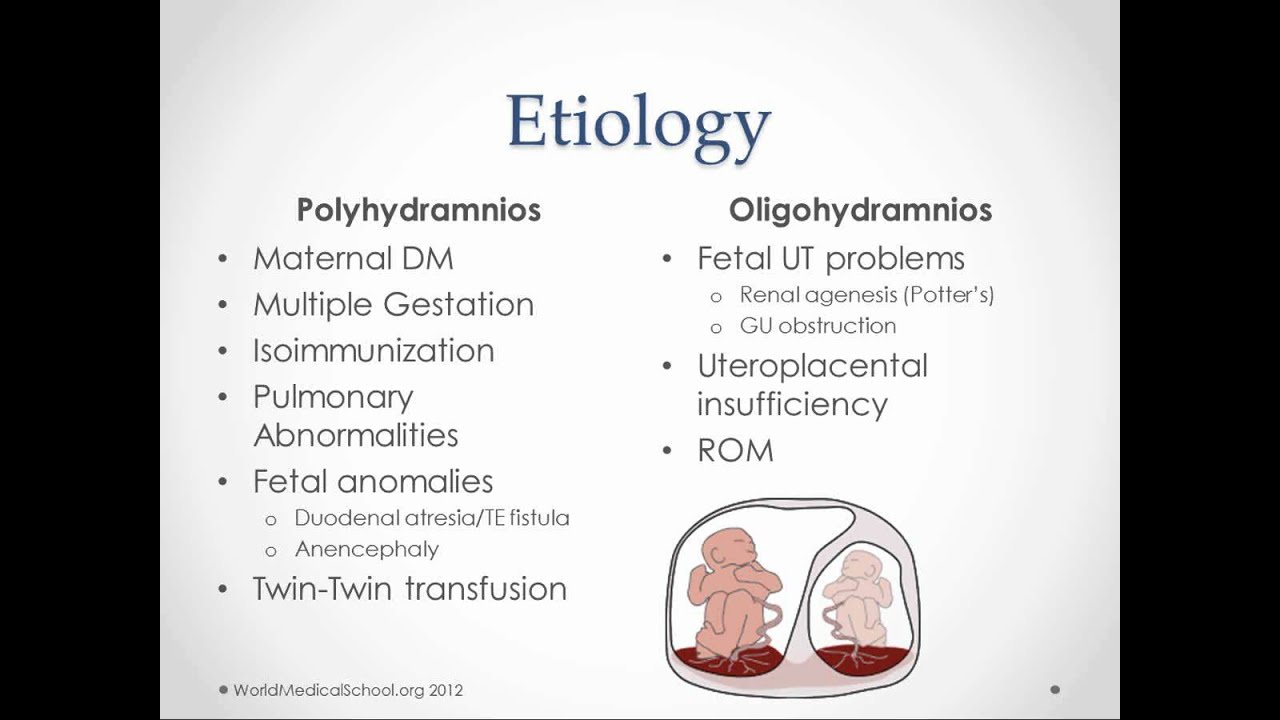
Polyhydramnios is a medical condition during pregnancy in which the amniotic fluid accumulates excessively. The amniotic fluid is the substance that surrounds the baby in utero. Excessive amounts of amniotic fluid may cause pressure within the uterus and also to the surrounding organs.

Oligohydramnios Etiology, Diagnosis, and Management UpToDate PDF
Overview What is oligohydramnios? Oligohydramnios occurs during pregnancy when your amniotic fluid is lower than expected for your baby's gestational age. Amniotic fluid is a water-like fluid that surrounds your baby in your uterus.

Oligohydramnios Nanda Nursing Diagnosis
The term oligohydramnios literally means "scant amniotic fluid" and is diagnosed when an ultrasound reveals an amniotic fluid index (AFI) of less than 5 cm. For reference, the normal value for AFI is 5-25 cm. What is amniotic fluid?

Oligohydramnios MedicoLearning
Oligohydramnios is amniotic fluid volume that is less than expected for gestational age; it is associated with maternal and fetal complications. Diagnosis is by ultrasonographic measurement of amniotic fluid volume. Management involves close fetal monitoring and serial ultrasonographic assessments. Causes of oligohydramnios include the following:

Oligohydramnios NCLEX Review Straight A Nursing
Oligohydramnios is the condition of having too little amniotic fluid. Doctors can measure the amount of fluid through a few different methods, most commonly through amniotic fluid index (AFI) evaluation or deep pocket measurements.

Oligohydramnios definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment
Oligohydramnios is defined as decreased amniotic fluid volume (AFV) for gestational age. The volume of amniotic fluid changes over gestation, increasing linearly until 34 to 36 weeks gestation, at which point the AFV levels off (approximately 400mL) and remains constant until term. [1]

What is Oligohydramnios? (Signs and Symptoms)
Oligohydramnios is defined as a deepest fluid pocket of less than 2 cm or an amniotic fluid index of 5 cm or less. It develops in 0.5-4.0% of all pregnancies and can be associated with fetal growth restriction as a result of reduced renal perfusion and urinary output.